今日推荐开源项目:《竟无语凝噎 dumb-password-rules》
今日推荐英文原文:《New Project? Just Hardcode It》

今日推荐开源项目:《竟无语凝噎 dumb-password-rules》传送门:GitHub链接
推荐理由:众所周知,设置密码的时候总是有些规则来帮助你提高安全性——从基本的不能纯数字到必须加入一个特殊符号等等,但是有些规则实在是有点让人无语……这个项目收集了拥有让人无语的密码规则的网站,有些前车之鉴还是不要再犯比较好,当作茶余饭后的趣闻一读也不错,毕竟限制密码为六个字符什么的实在是有点太让人无语凝噎了……
今日推荐英文原文:《New Project? Just Hardcode It》作者:Allen Helton
原文链接:https://medium.com/better-programming/new-project-just-hardcode-it-bac72e1a231e
推荐理由:在速度至上的时候,选择不去想太多也是一种选择
New Project? Just Hardcode It
Spending too much time building configuration nobody asked for? What about writing an extension point you’ll never use? Just hardcode it
If you follow my writing, you know I have two strong beliefs:- Time to market is the key to success
- Value iteration above all else
Have you ever been in a situation where your team committed to getting a project done in a certain amount of hours, but you went over because a piece of configuration was a bit more complicated than expected? And come to find out your clients don’t even use that configuration?
It’s frustrating to you because you spent all that time coming up with a robust set of configuration that nobody uses. It’s frustrating to your clients because you delayed getting their software because of configuration they don’t want.
So How Do We Change?
Hardcode it. Unless you specifically committed to building a piece of configuration, just hardcode it. Place value on iteration. Quickly get the product to your consumer. Let them see what they like and don’t like.You’ll be amazed how many people are happy without configuration they think they need.
Let’s take a look at an example. Your team is responsible for building a sandwich ordering app. The app presents users with a list of ingredients they can select before they hit submit. After they submit their order, it goes to the cooks who then process the order and deliver it to you via bicycle. Very 2019.

Image by Kai Pilger from Pixabay
But someone on your team has the idea to introduce a “the usual” concept. The user logs in, sets their ingredients for the sandwich they order all the time, and hits save. Now they have a one-click order option.
Somebody else suggests adding configuration for the cooks to mark when an ingredient is out of stock. Seems necessary so you don’t have orders missing ingredients, so you add that into the mix.
Another person brings up that you need a priority membership. People can pay to become pro members so their sandwich orders bump up to the top of the queue automatically. Pay more, wait less.
Before long, you have a list of features and configurations that have easily doubled or tripled your time to market if you build them all. What do you do now? Delay the release?
No.
Hardcode what you can. Omit the unnecessary features. Get some user testing in before building out all your features.
Build, measure, learn
In the book Lean Startup, the author talks about the principle of build, measure, learn. In short, it is a feedback loop that helps you iterate and improve your product.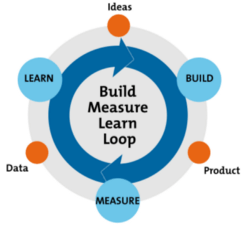
Diagram adapted from Ries, E. (2011) ‘The Lean Startup,’ New York: Crown Business.
Build something small. Measure feedback from customers. Learn from their needs. Then start the cycle over again. Build one of the needs you just learned about. Measure if you met the need. Learn how it can be improved.
In our sandwich app, all we need to do is display a list of ingredients and take payment. It displays the order on a screen to the cooks. The cooks mark the order complete. The bicyclist delivers the order. Iteration 1 complete.
Show it to your customers. Get their feedback. Turns out they really need the ability to mark ingredients out of stock. Learn where the priorities are. Go build it.
Maybe they never bring up the idea of “the usual.” You saved yourself time that you could have been innovating. By omitting or hardcoding features that could have been configurable, we allow ourselves to spend our time building what the customer truly wants.
Do People Really Do This?
Yes! Many companies are out there right now changing the world by building products and services that we actually need. In fact, if you take a look at the GitHub flow, you can see this is the model they follow.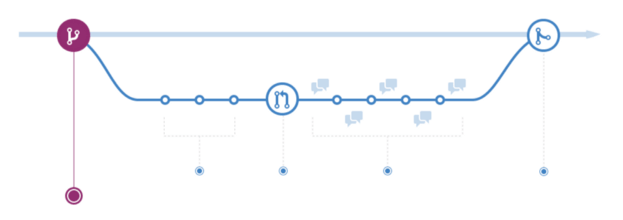
GitHub Flow from GitHub
The GitHub flow proposes that you deploy a new feature to production before merging it to master. So getting the feature out in front of your customer base before considering it gold or even feature complete is the main idea. Doing so enables you to verify the feature is something your customers will use.
What do you call software your customers are happy to use? A market success.
This is a strategy that many startups follow. You won’t be alone or trodding new ground if you go down this route. You will be joining the thousands of other companies in the happy customer club because you will be getting software they want to them quickly.
Call to Action
Don’t overthink it. Software doesn’t have to be hard. The best architects make simple solutions of complex problems. How do they do that? Hardcoding it. They don’t dirty up the water with unnecessary configuration.They get the problem solved the fastest they can to get exposure. They measure their success from the feedback of their customers. They learn about the needs and new features that are necessary.
I’m not saying you need to throw everything away you’re currently doing, but consider being more agile and getting your customers exposed to ideas earlier in the process. Don’t let you hold you back. Value iteration. Value simplicity. Value a market success.
下载开源日报APP:https://openingsource.org/2579/
加入我们:https://openingsource.org/about/join/
关注我们:https://openingsource.org/about/love/
