今日推荐开源项目:《它不会直接教你玩摄影 awesome-OpenSourcePhotography》
今日推荐英文原文:《Understanding SQL Injections》

今日推荐开源项目:《它不会直接教你玩摄影 awesome-OpenSourcePhotography》传送门:GitHub链接
推荐理由:一个关于摄影方面知识和工具的集合——说是这么说,但是它并不会教你如何拍照就是了。准确的说这个项目中提供了很多关于照片和视频方面的知识和工具——包括处理照片和视频以及照片管理等等,当然了也包括一些工具和库。如果你需要处理一些与照片和视频有关的工作的话,兴许这里可以找到你想要的东西。
今日推荐英文原文:《Understanding SQL Injections》作者:Scott Cosentino
原文链接:https://medium.com/@scottc130/understanding-sql-injections-47049fcf9acb
推荐理由:关于一个常见的漏洞——SQL注入,如果有在使用数据库的话就需要想办法防止这种情况的产生了。
Understanding SQL Injections
Code injection vulnerabilities are rated as the most common vulnerability according to the OWASP 2017 Top 10 List. Most commonly, SQL injections are used to compromise databases and applications, in order to cause data leaks and unauthorized access. As someone involved in the field of tech, it is essential that you understand this vulnerability, so you can actively prevent it from happening to your applications.To best understand the vulnerability, let’s build a sample database and application, and see how SQL interacts with the typical application. Suppose we have a simple SQL database, with a table called users, defined below:

Query to create user tableIn this table, we will insert some sample users to have some data to work with:
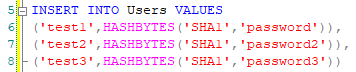
Query to insert users and hashed passwordsWe now have a database similar to one that might be used for authentication on any application. To see how we can interact with the database, I will create a basic VB.net application. Here we have a simple login form:
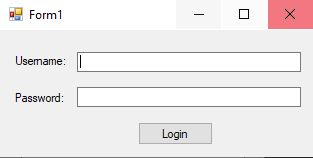
Login form for applicationAnd some code that will take input from the form and check if the username and password supplied exist in the database:
Dim sqlCommand as SqlCommand
Dim username As String
Dim password As String
username = usernameTextbox.Text
password = passwordTextbox.Text
sqlConnection.Open()
sqlCommand = New SqlCommand("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Users WHERE Username = '" & username & "' AND userPassword = HASHBYTES('SHA1','" & password & "')", sqlConnection)
If sqlCommand.ExecuteScalar() > 0 Then
MsgBox("Login Successful")
Else
MsgBox("Login Failed")
End If
To start, the user inputs their credentials, and presses “Login”
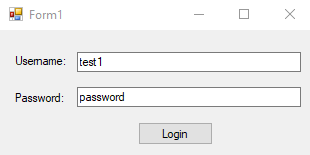
User inputs credentialsOnce login is pressed, the SQL query to check the user is built by concatenating the username and password inputs into a query, and running it against the database. The end SQL query looks like this:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Users
WHERE Username = 'test1'
AND userPassword = HASHBYTES('SHA1','password')
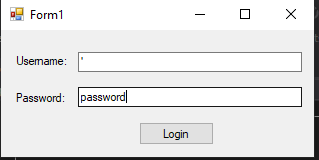
User inputs ‘ as usernameNow, the query would be built as:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Users
WHERE Username = '''
AND userPassword = HASHBYTES('SHA1','password')
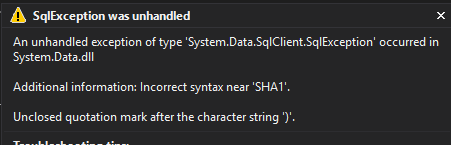
SQL exception for queryWe get an SQL exception telling us that our query syntax is incorrect! So how is this possible? When the user inputs the ‘ character, it is concatenated to the query, and the query is run against the database. SQL is interpreting the ‘ character as a closing quote for the username string, causing a mismatch in quotes and therefore a syntax error in the query.
Already, this situation is bad, as the user can cause the program to crash just by entering a single character. However, it gets worse. The user can do a lot more damage by altering the query completely.
Consider the input shown below:
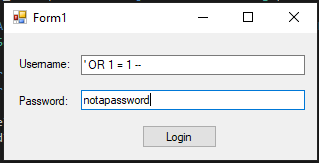
Malicious user inputIf the attacker were to enter these values, the query that results from it would be:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Users
WHERE Username = ''
OR 1 = 1 -- '
AND userPassword = HASHBYTES('SHA1','notapassword')
The result of this query is to return the count of everything in the Users database. Since this is going to be greater than 1, the user will be authenticated with access, even though they did not enter valid credentials!
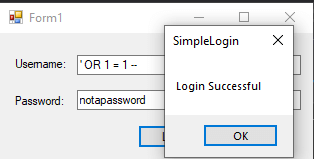
User is given accessThis is obviously bad news, as we never want a user to be able to gain access to an application without proper credentials. So, how do we avoid this issue?
Some people might suggest removing any ‘ character, however this might be a valid input (consider a name like O’Reily). This being the case, there is a better solution.
The best answer to this problem is parameterized queries. Parameterized queries will generate the SQL execution plan before input is added, meaning it will avoid executing code inputted by the user. If we wanted to modify our original code to use parameterized queries, we could do so as follows:
Dim sqlCommand As SqlCommand
Dim query As String = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Users WHERE Username = @username AND userPassword = HASHBYTES('SHA1',@password)"
Dim username As String
Dim password As String
username = usernameTextbox.Text
password = passwordTextbox.Text
sqlConnection.Open()
sqlCommand = New SqlCommand(query, sqlConnection)
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add("@username", SqlDbType.VarChar, 300).Value = username
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add("@password", SqlDbType.VarChar, 300).Value = password
If sqlCommand.ExecuteScalar() > 0 Then
MsgBox("Login Successful")
Else
MsgBox("Login Failed")
End If
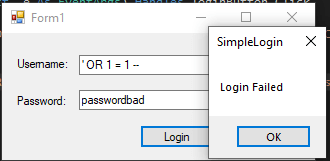
User is now rejected accessThe parameterized version of the query is significantly more secure, and will help you be safe from SQL injection attacks. It is important to use this method when accessing SQL databases, otherwise your data may be destroyed or improperly accessed by attackers!
下载开源日报APP:https://openingsource.org/2579/
加入我们:https://openingsource.org/about/join/
关注我们:https://openingsource.org/about/love/
