开源日报每天推荐一个 GitHub 优质开源项目和一篇精选英文科技或编程文章原文,坚持阅读《开源日报》,保持每日学习的好习惯。
今日推荐开源项目:《Outfit Anyone》
今日推荐英文原文:《How I Answered “What is Virtual DOM in React?” in My Interview 🤔》

开源项目
今日推荐开源项目:《Outfit Anyone》传送门:项目链接
阿里ai大模型通义实验室XR的研究成果 :Outfit Anyone
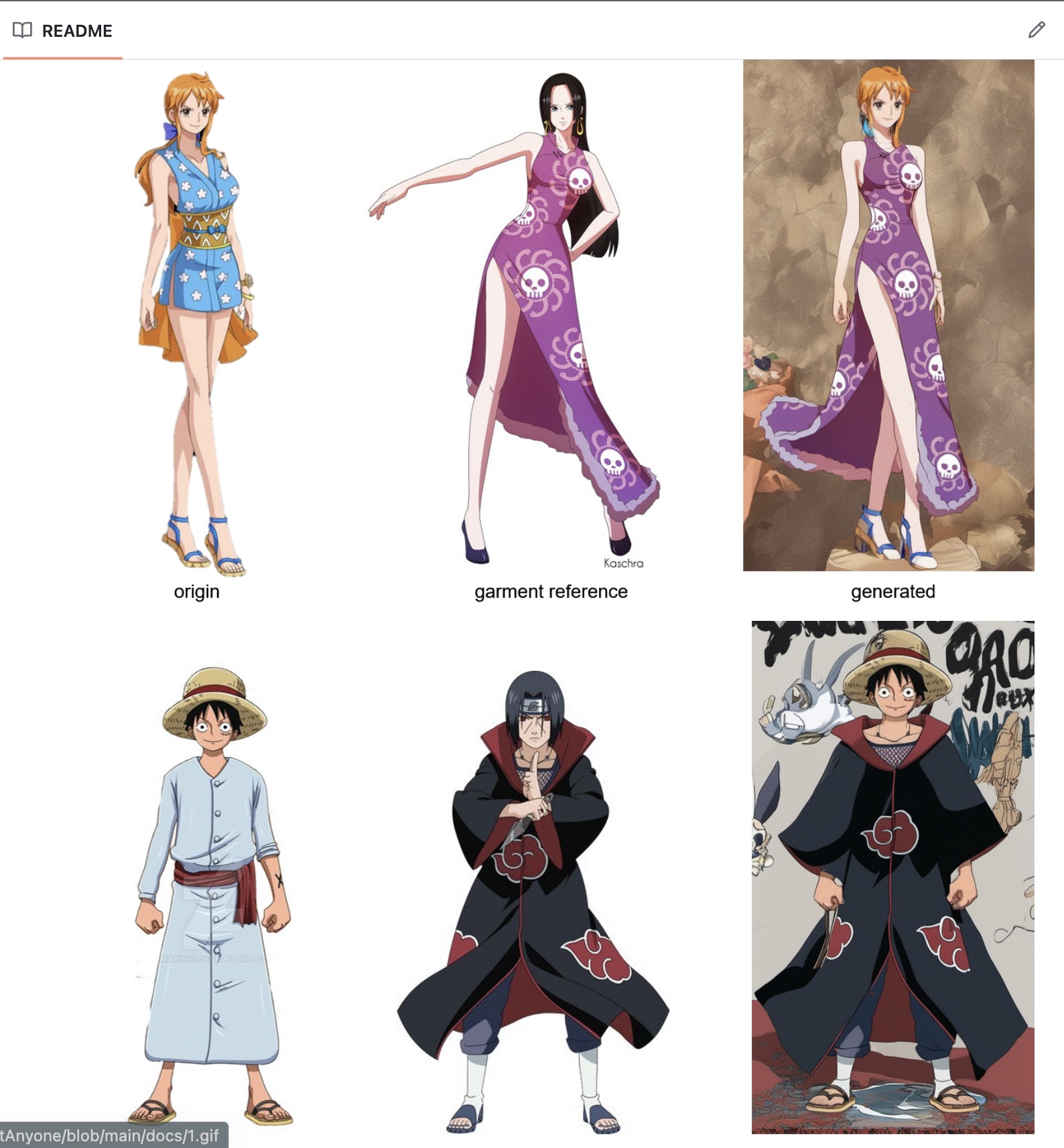

基于AIGC给modal穿上自定义服装,目前仍处于开发阶段,可以尝尝鲜
英文原文
今日推荐英文原文:How I Answered “What is Virtual DOM in React?” in My Interview 🤔
经典面试题: react的虚拟dom是如何工作的,非常实用
How I Answered “What is Virtual DOM in React?” in My Interview 🤔
Introduction 🚀
When I was asked about the Virtual DOM in React during an interview, I realized it’s a fundamental concept that often confuses beginners. Understanding the Virtual DOM is crucial for React developers as it is the foundation of React’s high performance and efficient rendering process, enabling the creation of dynamic and responsive user interfaces with minimal impact on browser performance.
In this blog, I’ll share how I explained it in simple terms, along with a practical example.
Understanding the Virtual DOM 🌱
The Virtual DOM is a core concept in React that significantly enhances the performance and efficiency of web applications. It’s a lightweight representation of the actual DOM (Document Object Model) in memory. The key difference between the Virtual DOM and the Real DOM is in their updating process. The Real DOM updates are slow and inefficient, especially with large applications or frequent changes, leading to performance issues.
React uses this Virtual DOM to enable a smooth user experience. Here’s how it works: Whenever there’s a change in a component’s state, React first reflects this change in the Virtual DOM. Then, instead of updating the Real DOM immediately, React employs a Diffing algorithm. This algorithm compares the updated Virtual DOM with a snapshot of the Virtual DOM before the update, effectively identifying exactly what changed.
This process, known as reconciliation, is where React shines. It updates the Real DOM based on these differences, doing so in the most efficient way possible. This minimizes direct manipulation of the Real DOM, which is a costly operation in terms of performance.
JavaScript updating: Real DOM Example 💡
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="text">Initial Text</p>
<button id="updateButton">Click Me</button>
<script> document.getElementById("updateButton").addEventListener("click",()=> {
document.getElementById("text").innerText = "Updated Text";
}); </script>
</body>
</html>In this HTML and JavaScript example, clicking the button changes the text of the paragraph to “Updated Text.” Each click triggers the update, and you can see these changes reflected in the browser’s Elements panel. This is because every update directly manipulates the Real DOM, even if the content being updated is the same.
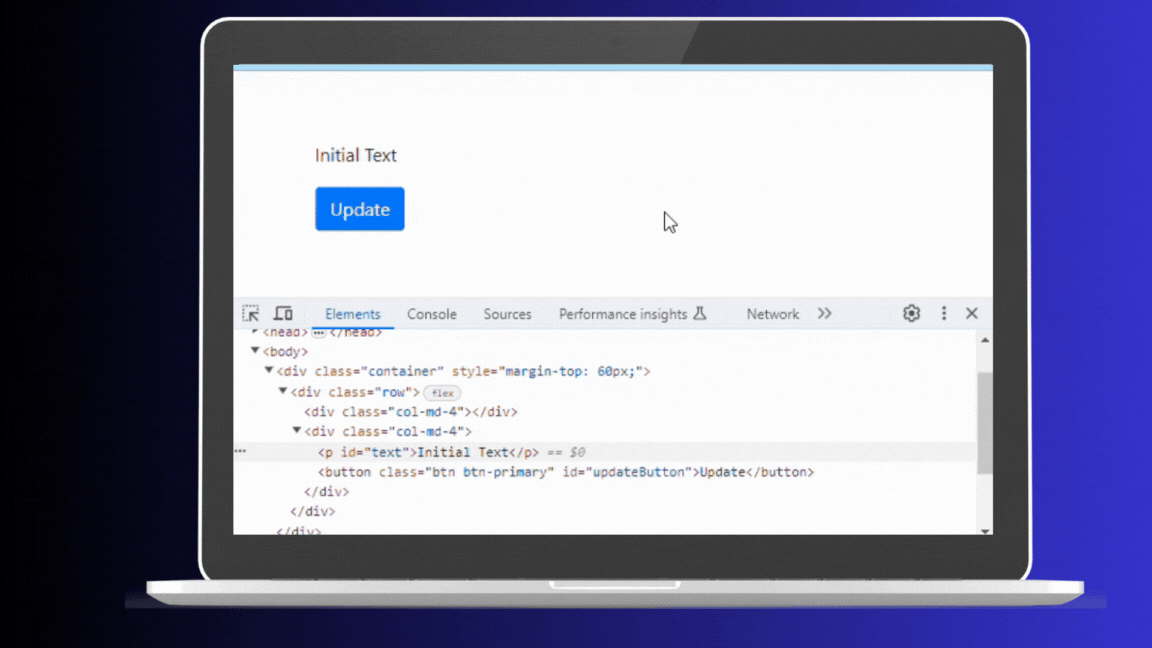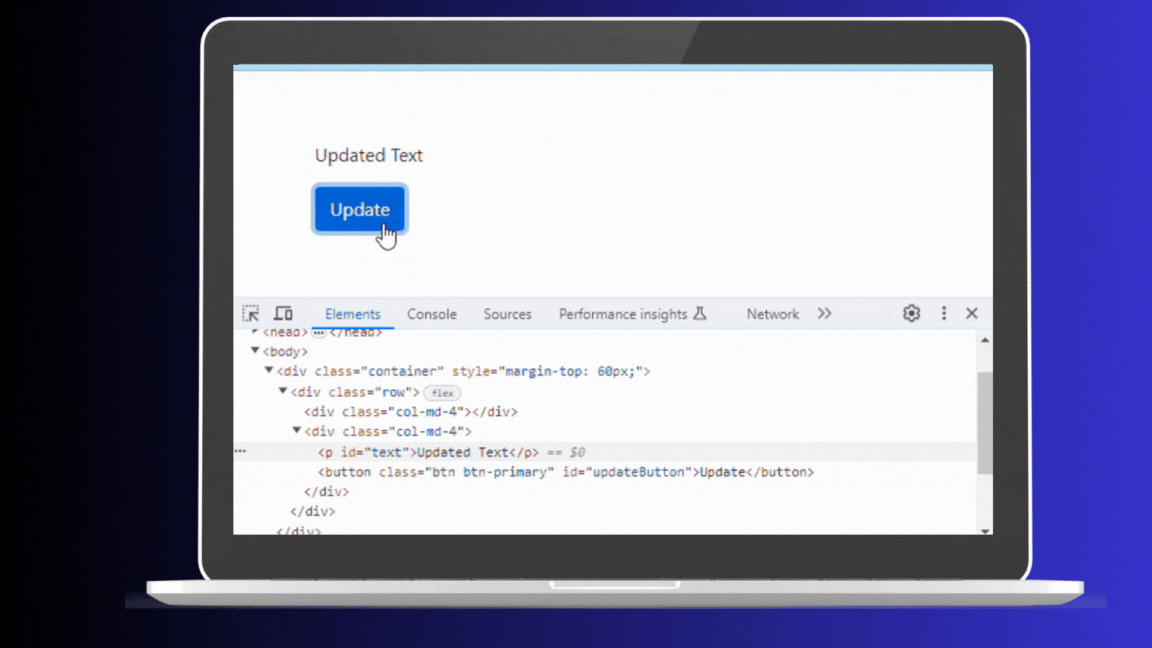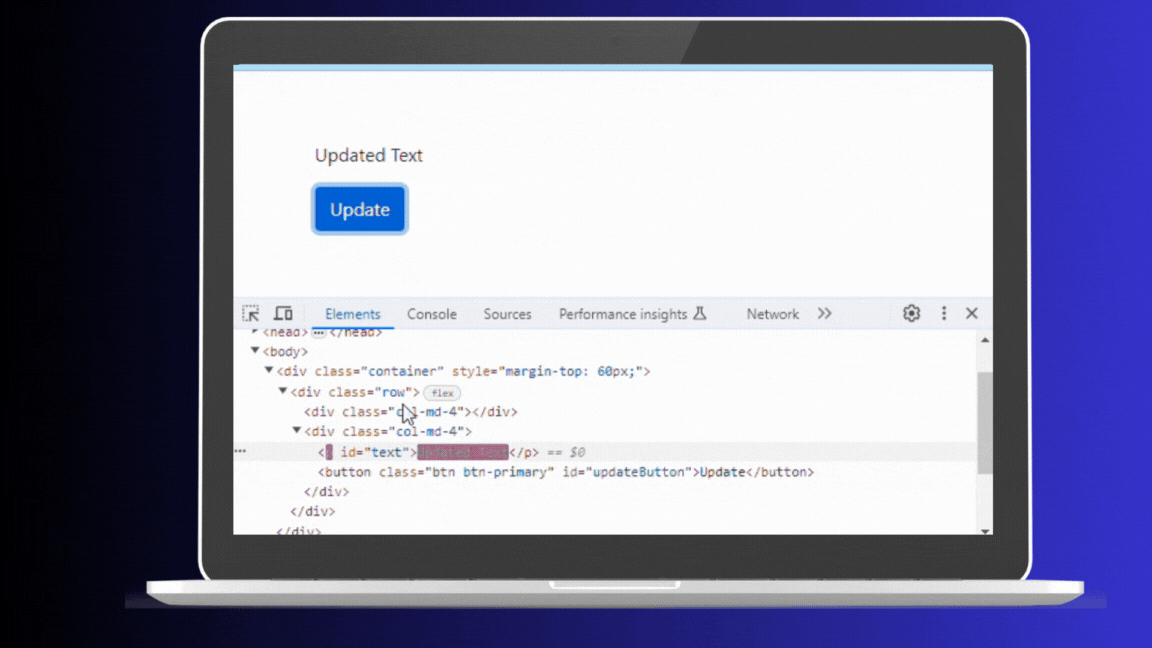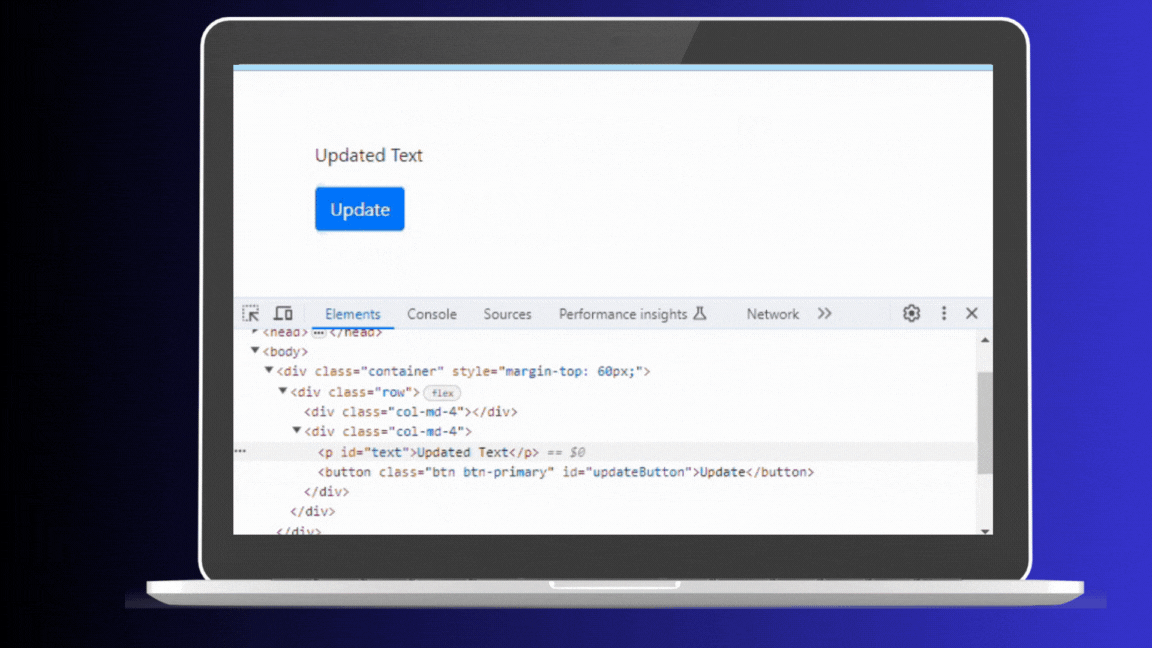
Real Dom Updates
React Example: Updating Content with Virtual DOM 🧩
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function App() {
const [text, setText] = useState('Initial Text');
const handleClick = () => {
setText('Updated Text');
};
return (
<div>
<button onClick={handleClick}>Click Me</button>
<p>{text}</p>
</div>
);
}
export default App;In this updated example, we define a handleClick function in the component. When the button is clicked, this function is executed, which then calls setText to update the state. This is a common pattern in React for handling events. The outcome in terms of DOM updates remains the same as the previous example: React's Virtual DOM will only update the Real DOM on the first click, as subsequent clicks do not change the state (the text remains "Updated Text"). This demonstrates React's efficiency in handling DOM updates through its reconciliation process.

Virtual DOM in react
Conclusion ❤️
In this blog, we explored the Virtual DOM in React, a concept that might seem complex at first but is actually pretty straightforward once you understand it. Remember, the Virtual DOM is like a lightweight copy of the real web page you see in your browser. It helps React update what you see on screen quickly and efficiently, without slowing things down. This is super important for making websites that are fast and smooth. By using examples, we saw how React updates only what’s necessary, instead of changing everything, which is what makes it so special. Keep practicing and exploring React, and soon, the Virtual DOM will become a familiar friend in your journey as a web developer. Happy coding!
下载开源日报APP:https://openingsource.org/2579/
加入我们:https://openingsource.org/about/join/
关注我们:https://openingsource.org/about/love/
