開源日報每天推薦一個 GitHub 優質開源項目和一篇精選英文科技或編程文章原文,堅持閱讀《開源日報》,保持每日學習的好習慣。
今日推薦開源項目:《Best-websites-a-programmer-should-visit》
今日推薦英文原文:《Fetch Data in React JS in Modern Way》

開源項目
今日推薦開源項目:《Best-websites-a-programmer-should-visit》傳送門:項目鏈接
非常好的閱讀材料,編程導航,內涵很多程序員必備的專業知識,但也不局限於。
合格的programmer不僅是技術優良,還有很多軟技能需要掌握
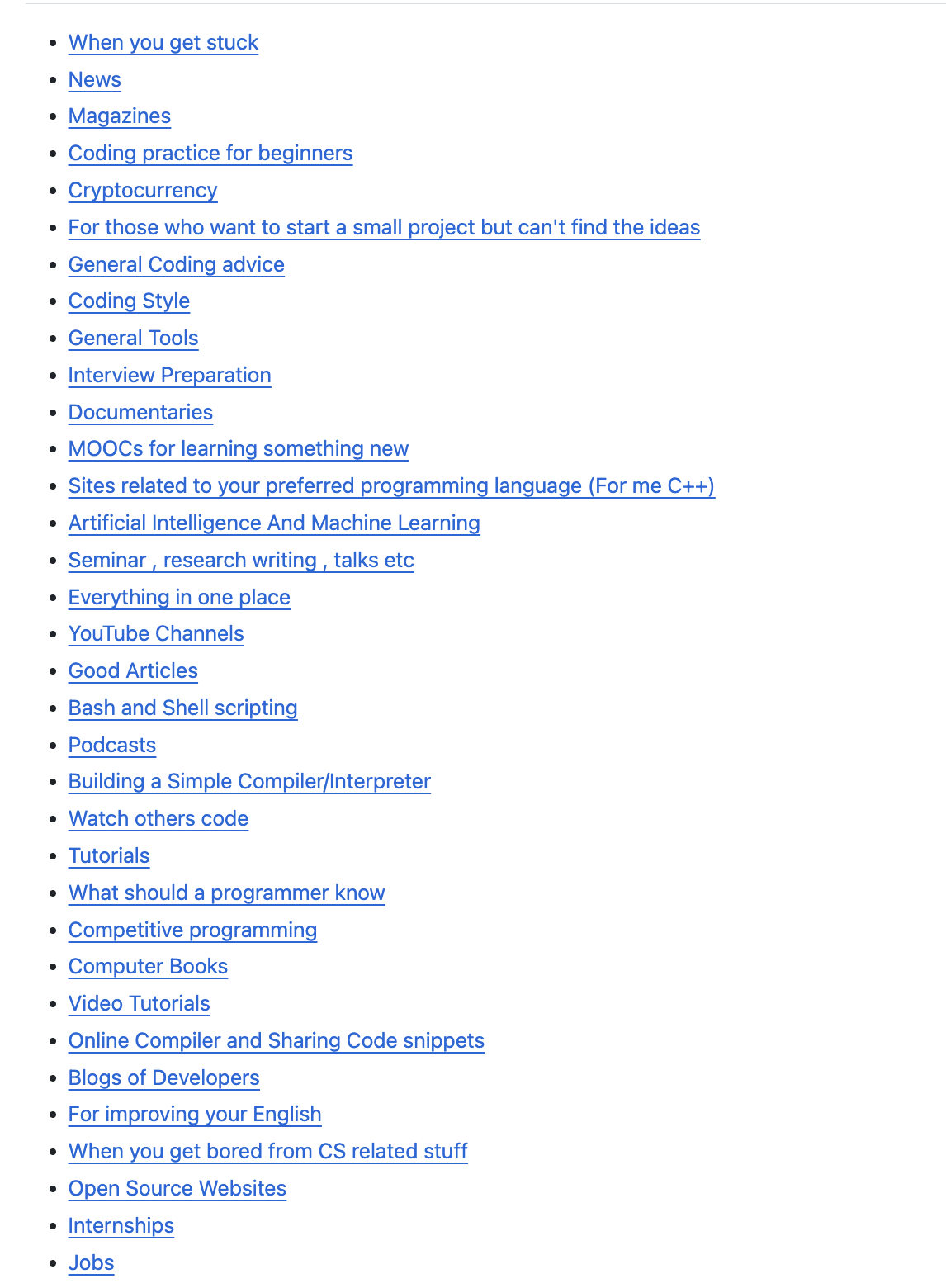
倉庫的目錄:
英文原文
今日推薦英文原文:Web workers in React
推薦理由:介紹了webWorker的基本使用方法和使用場景,適用於前端mock 假數據快速開發
Web workers in React
Have you ever faced a situation in which you are executing a block of code and it is freezing the UI for a few seconds? If yes then you surely need a solution to handle that block of code in the background.
In React we have a simple way to do these types of CPU-intensive processes in the background with the help of web workers. First of all what a web worker is?
A web worker is a JavaScript feature that allows you to run scripts in the background, separate from the main thread of your web page. This background execution enables you to perform tasks concurrently without blocking the user interface (UI) or causing it to become unresponsive. Web workers are particularly useful for handling computationally intensive or time-consuming operations without impacting the user』s experience.
The use cases for a web worker are
- Complex Calculations: Web workers are ideal for performing complex mathematical calculations or data processing tasks without impacting the main thread.
- Large Data Handling: When dealing with large datasets or files, web workers can help process and parse the data in the background.
- Background Services: Web workers can be used to run background services such as periodic data synchronization or background notifications.
So, let』s try to implement a web worker in a React application.
First, we create a react project, and then we use a service faker to create 25000 user records.
import { faker } from '@faker-js/faker';
export function fetchUsers() {
const users = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 25000; i++) {
let id = i + 1;
let name = faker.person.fullName();
let email = faker.internet.email();
let joinedOn = faker.date.recent();
let commentCount = faker.number.int({ min: 0, max: 100 });
let user = {
id,
name,
email,
joinedOn,
commentCount
};
users.push(user);
}
return Promise.resolve(users); }
Now, our goal is to sort these records ascending and descending based on 「commentCount」 by using a web worker.
So, first, we will create two files 「src/app.worker.js」 and 「src/WebWorker.js」.
In the 「app.worker.js」 file we will export an arrow function in which we will add an event listener on the window object(self) to listen to the 「message」. This 「message」 will be triggered from the UI with 「users」 and 「type」(ascending or descending」 variables.
export default () => {
self.addEventListener('message', e => { // eslint-disable-line no-restricted-globals
if (!e) return;
let { users, type } = e.data;
if(type === "asc") {
users = users.sort((a, b) => a.commentCount - b.commentCount);
} else {
users = users.sort((a, b) => b.commentCount - a.commentCount);
}
postMessage(users); })
}
And we will sort it according to the 「type」 variable and return it by 「postMesssage」 method.
And in the 「WebWorker.js」 we will export a class.
constructor(worker) {
const code = worker.toString();
const blob = new Blob(['('+code+')()']);
return new Worker(URL.createObjectURL(blob));
} }
It will simply change the worker we defined in 「app.worker.js」 to an object URL.
Now, let』s connect this webworker to the UI.
First, we will import both the 「worker」 and 「WebWorker」 from the respective files.
import worker from './app.worker.js';
import WebWorker from './WebWorker';
Then, we will initialize the 「WebWorker」 with the argument 「worker」.
const webWorker = new WebWorker(worker);
First, we will work on the ascending logic. So, we will send the 「users」 and 「type」 to the worker by the 「postMessage」 method on this web worker.
webWorker.postMessage({ users, type: "asc"});
Then, we will listen to the 「message」 and get the sorted data from the web worker like this.
webWorker.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
const sortedList = event.data;
setUsers(sortedList);
});Same logic we will add for the descending function as well.
webWorker.postMessage({ users, type: "desc"});
webWorker.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
const sortedList = event.data;
setUsers(sortedList);
});So, now our sorting is working fine. But don't forget to terminate the web worker at the time of component unmounting.
return () => {
webWorker.terminate()
}
So, finally, our application will look something like this.
下載開源日報APP:https://openingsource.org/2579/
加入我們:https://openingsource.org/about/join/
關注我們:https://openingsource.org/about/love/
